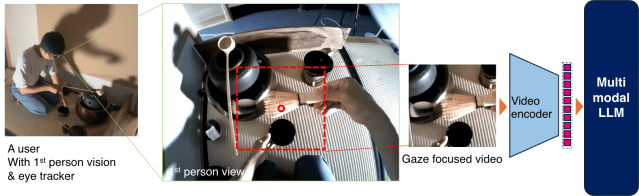
Large Language Models (LLMs) are advancing into Multimodal LLMs (MLLMs), capable of processing image, audio, and video as well as text. Combining first-person video, MLLMs show promising potential for understanding human activities through video and audio, enabling many human-computer interaction and human-augmentation applications such as human activity support, real-world agents, and skill transfer to robots or other individuals. However, handling high-resolution, long-duration videos generates large latent representations, leading to substantial memory and processing demands, limiting the length and resolution MLLMs can manage. Reducing video resolution can lower memory usage but often compromises comprehension. This paper introduces a method that optimizes first-person video analysis by integrating eye-tracking data, and proposes a method that decomposes first-person vision video into sub areas for regions of gaze focus.
By processing these selectively gazed-focused inputs, our approach achieves task comprehension equivalent to or even better than processing the entire image at full resolution, but with significantly reduced video data input (reduce the number of pixels to one-tenth), offering an efficient solution for using MLLMs to interpret and utilize human skills.
– 🚀 **MLLMの進化**: LLMはマルチモーダル(MLLM)へ進化し、画像・音声・動画を処理可能に。
– 🎥 **一人称視点×MLLM**: 一人称動画を活用し、人間の活動理解を向上。HCIやスキル移転に応用。
– 🧠 **高負荷の課題**: 高解像度・長時間動画の処理には大量のメモリ・計算資源が必要。
– 📉 **解像度低下のジレンマ**: 動画解像度を下げれば負荷軽減可能だが、理解度が低下。
– 👀 **視線追跡で最適化**: 視線データを活用し、注視領域ごとに動画を分割・処理。
– 🎯 **効率的な処理**: 画素数を1/10に削減しつつ、全体画像と同等以上の理解を実現。
